
If your child tries to climb into your bed at night, unless he is afraid, return him to his bed as soon as you discover his presence.If the child says he is in bed, open the door. Using good eye contact, tell the child that you will open the door again when the child is in bed.
If your child comes out of his room, avoid lecturing him.If your child starts screaming, shut the door to his bedroom and say, "I am sorry, but I have to shut your door.Establish a rule that the child cannot leave the bedroom.Once the door has been closed, it is best to ignore further requests. Before you turn out the light, ask if the child needs anything else.A stuffed animal or special blanket may give the child some security after the lights are turned out.Give your child a warning when it is almost time for lights-out and sleep. Keep the routine to a set amount of time each night.Choose activities that are calming, such as taking a bath, reading, or giving a gentle massage.Keep activities such as taking a bath, brushing teeth, reading stories, saying prayers, and so forth in the same order every night.

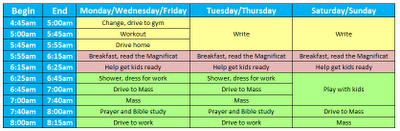
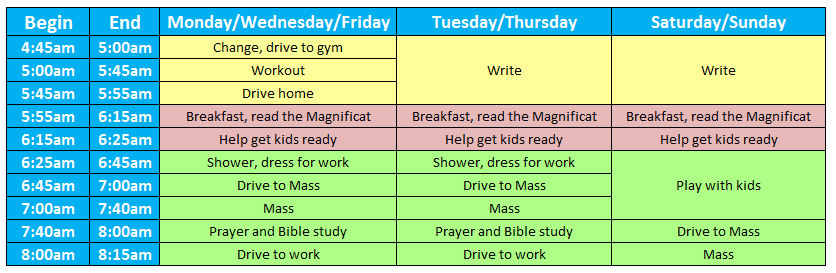
Make the bedtime routine pleasant and predictable. By around 18 months, children only need one nap each day. Sleeping with a baby younger than 12 months of age may increase the risk for SIDS.Ī toddler will most often sleep for 12 to 14 hours a day. However, over time, your infant will learn to self-soothe and fall back asleep. Infants will still wake up during the night. If you maintain this routine, your baby will become used to it and go to sleep on his own.īy age 9 months, if not sooner, most infants are able to sleep for at least 8 to 10 hours without needing a nighttime feeding.
Signs that your baby is becoming sleepy include: They stay awake only 1 to 3 hours at a time. Newborns may sleep between 10 and 18 hours a day. YOUR NEW BABY (LESS THAN 2 MONTHS) AND SLEEPĪt first, your new baby is on a 24-hour feeding and sleep-wake cycle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
